
Learning retention refers to the ability of individuals to retain and remember information, knowledge, and skills they have acquired through the learning process. It involves the long-term storage and application of learned content, ensuring that learners can recall and apply what they have learned over time.
Various factors contribute to learning retention, including the use of effective instructional techniques, active engagement in the learning process, reinforcement, and practice, and creating connections and relevance to real-world applications.
Learning Pyramid
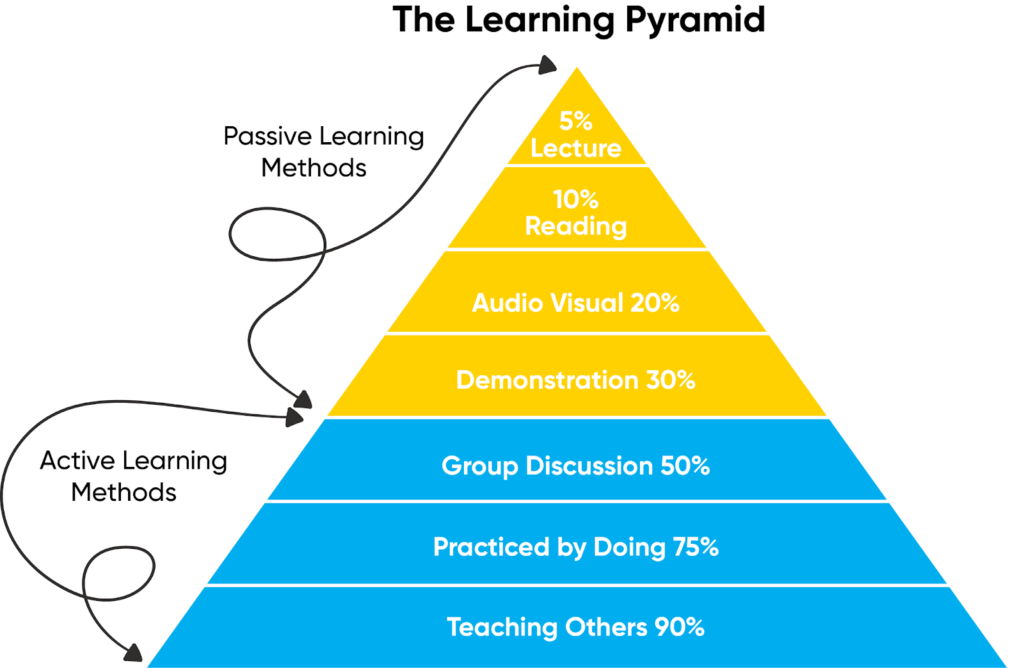
The learning retention pyramid, also known as the cone of learning or the pyramid of retention, is a theoretical model that illustrates the various methods of learning and their respective expected percentages of retention.
The pyramid suggests that different learning methods have different degrees of effectiveness in promoting long-term retention of information.
The principles of learning retention can vary depending on the context and sources.
However, some common principles include:
-
- Active engagement
Learners retain information better when they actively engage in the learning process through activities, discussions, and application.
2. Relevance and meaning
Learning is more likely to be retained when it is perceived as relevant and meaningful to the learner’s interests, goals, and experiences.
-
- Repetition and practice
Repeated exposure and practice of learned material help reinforce memory and enhance retention.
-
- Chunking
Breaking down complex information into smaller, manageable chunks can aid retention and facilitate understanding.
-
- Retrieval practice
Regular retrieval of learned information through quizzes, tests, or recall exercises strengthens memory and improves retention.
-
- Spaced repetition
Distributing learning and review sessions over time, with increasing intervals between sessions, promotes long-term retention.
-
- Visual aids and multi-modal learning
Incorporating visual aids, multimedia resources, and multi-modal approaches (e.g., combining text with images or audio) can enhance comprehension and retention.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of these principles may vary among individuals and learning contexts.
Therefore, it is beneficial to consider individual learning preferences and adapt instructional strategies accordingly.
Its an experiential learning and practicing with the focus on the following strategies in my training/workshop setting.
-
- Pre-assessment and goal setting
-
- Active learning techniques
-
- Microlearning
-
- Real-world context and application
-
- Continuous reinforcement
-
- Gamification
-
- Learning support and resources
-
- Regular knowledge checks
-
- Follow-up opportunities
In conclusion, fostering effective learning retention is not just about acquiring knowledge but also about embedding it into one’s long-term memory for practical application. By embracing active engagement, relevance, repetition, and other proven principles, we pave the way for lasting learning outcomes.
In my training workshops, I prioritize experiential learning and employ strategies such as pre-assessment, active learning techniques, microlearning, real-world application, continuous reinforcement, gamification, and more. Together, these methods create an immersive and impactful learning environment.
For further insights and to stay updated on upcoming workshops and valuable content, follow me on LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/in/madhuri-krishnamurty. Let’s embark on this journey of continuous learning and growth together!
